Japanese firms Denso and KDDI say that they have begun researching 5G’s use in automated driving applications with the commencement of a verification project.
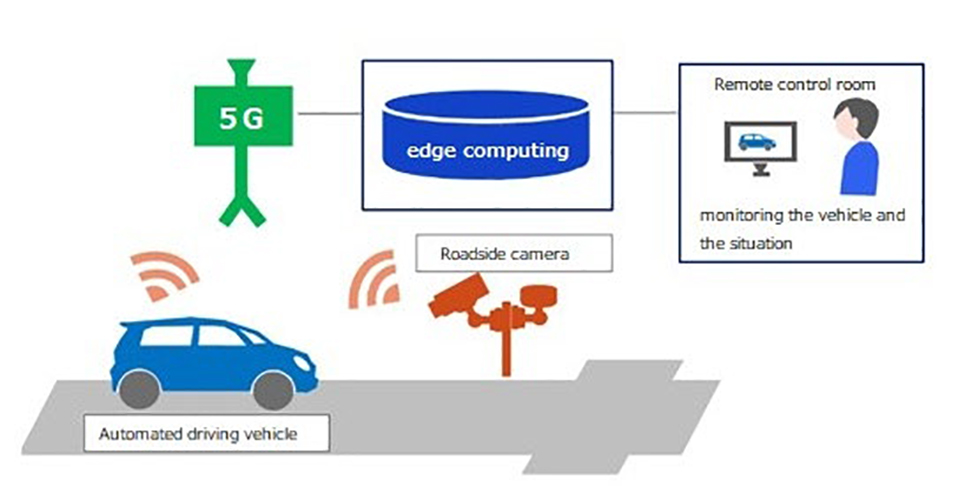
During the project, the two companies will build a 5G environment around the test course at Global R&D Tokyo, Haneda, a research and development center for automated driving, operated by Denso. Here, they will verify driver assistance technologies in automated driving vehicles using high-definition in-vehicle cameras and roadside sensors.
This will include the verification of systems for efficiently monitoring vehicles and their surroundings using high-definition images from in-vehicle cameras and roadside sensors based on a 5G communication network. The companies state they will leverage low-latency connections, which are achieved through edge computing technology for 5G, including AWS Wavelength, to build a system for distributing data to autonomous vehicles in real time and to verify the remote driver assistance technology.
Their plan is to conduct verification using end-to-end (E2E) network slicing. This technology provides the ability to tailor communication environment preferences, depending on the application and requirements, by virtually partitioning a network.
More broadly, the verification project also aims to promote the use of 5G in automated driving applications by combining Denso’s know-how in developing in-vehicle communication technologies and KDDI’s expertise in advanced network technologies.